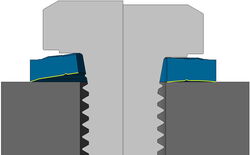
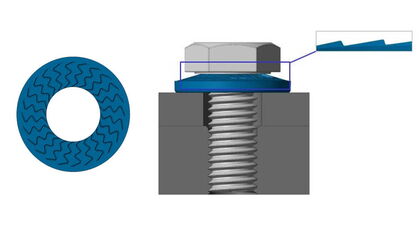
SK-ZCylinder head screws
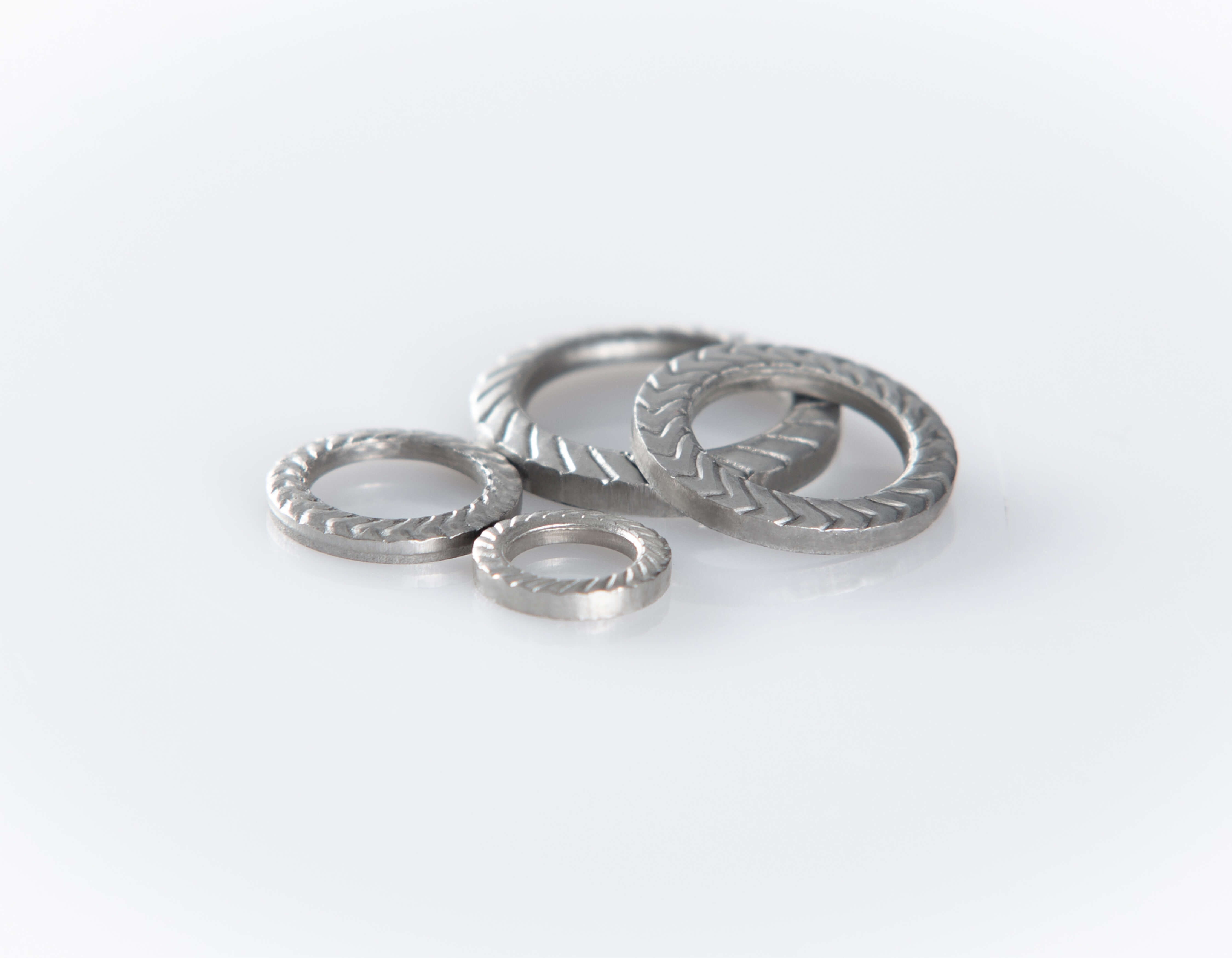

Areas of application
- Force-fit screw connections for static and dynamic transmission of the operating load via the braced components
- Cheese head screws
Special features
- Defined, constant coefficient of friction
- Increases the flexibility of the screw connection
- Locking element to prevent loosening & automatic unscrewing
Comparison of possible solutions for cylinder screw connections
| Spring/profile Locking edge ring1 Spring washer2 with washer |
Toothed disc (DIN 6798 / 6907) |
Serrated lock washer (DIN 6797/ 6906) |
Clamping disc (DIN6796) |
Locking edge disc SK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Damage to the counterclaims |
|
|
|
|
|
| Defined / reproducible contact pressure (coefficient of friction) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Improved compliance with short clamping lengths |
|
|
|
|
|
| Compensation of slackening effects3 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Compensation of loosening effects4 |
|
|
|
|
|
| State of the art5 |
|
|
|
|
|
1
DIN 127, 128, 6905, 7980 etc.
2
DIN 137, 6904
3
based on VDI 2230, DIN 267-26
4
in accordance with DIN 65151 / DIN 25201 - 4
5
Conformity with applicable standards / prerequisite for CE labelling
Executions
| Spring steel C60 EN 1.1211 |
Stainless steel A41 EN 1.4401 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Hardness / Strength | ≥ 430 HV10 | ≥ 595 N/mm2 |
| Coating | Zinc flake coating | - |
| Corrosion protection | > 720h in the salt spray test (according to ISO 9227) | PREN 27 (related to base material) |
| Temperature range | -40°C to 150°C | -40°C to 150°C |
| Screw quality | Cylindrical head bolts up to 8.8 | Cylindrical head bolts up to A4-70 |
| Dimension range | M6 - M16 | M6 - M16 |
1
can also be used for stainless steel A2 screws, e.g. EN 1.4301 or EN 1.4310
Anwendungsbereiche



Why do screw connections come loose?
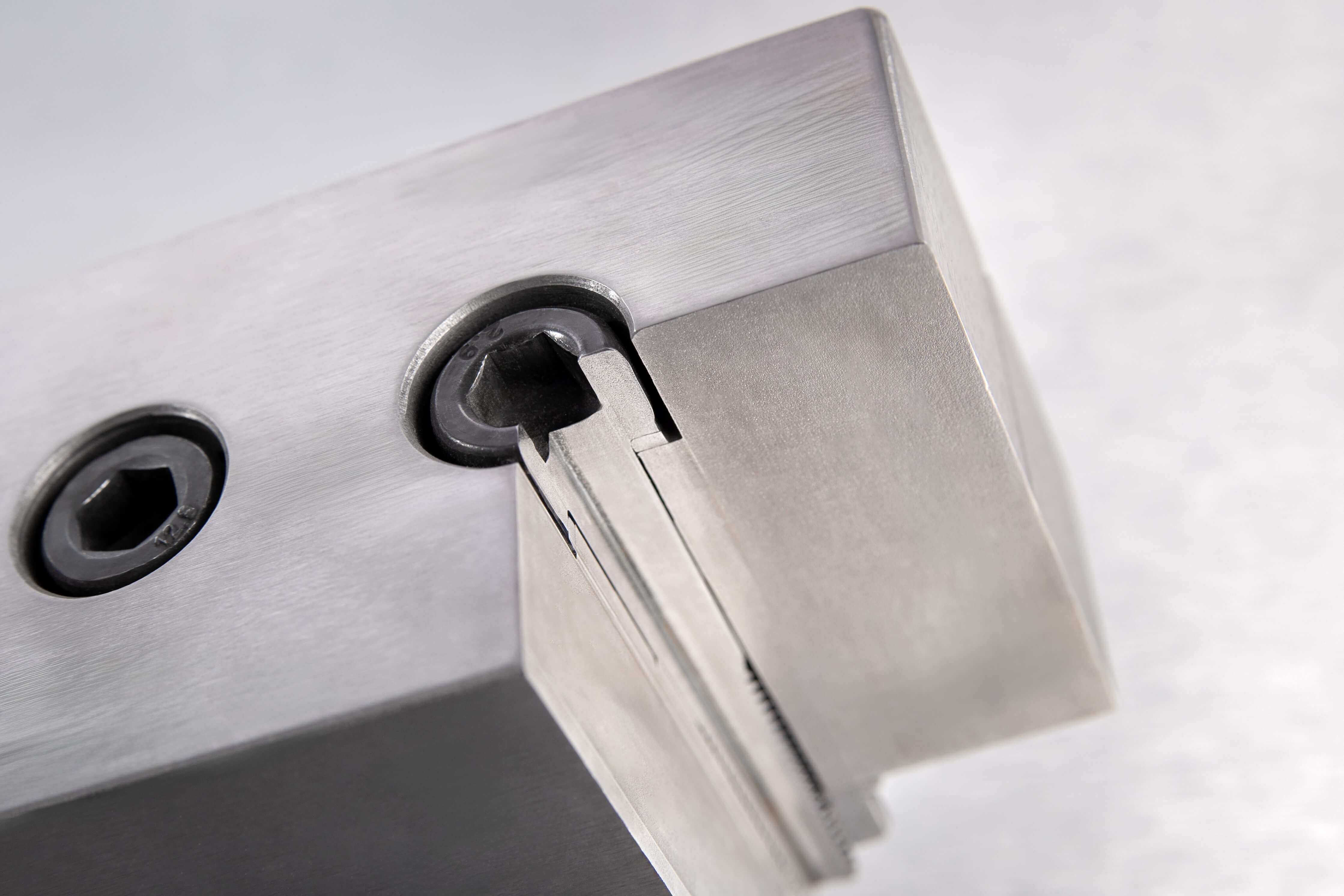
How does an SK-Z work?
Force-locking effect with curved geometry matched to the preload force depending on the strength class.
- Increases the flexibility of a bolted joint
- Prevents slackening effects and supports the locking effect against selfacting loosening
Form locking effect due to the interlocking under the screw head or on the nut.
- Supports the locking effect against selfacting loosening
Spring steel (C60) with zinc flake
| SK-Z | Article No. | DI | DA | S1 | H | Weight/1.000 St. | Pcs. per unit | 3D Download | Request |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SK-Z6 | 090630 | Ø 6.10+0.48 | Ø 9.90-0.36 | 1.40±0.10 | 1.60+0.20 | 0,50 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z8 | 090640 | Ø 8.20+0.58 | Ø 12.70-0.36 | 1.40±0.10 | 1.70+0.20 | 0,90 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z10 | 090650 | Ø 10.20.0.58 | Ø 16.10-0.36 | 1.60±0.10 | 2.00+0.20 | 1,50 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z12 | 090660 | Ø 12.40+0.58 | Ø 18.30-0.52 | 1.80±0.10 | 2.40+0.20 | 2,00 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z14 | 090670 | Ø 14.40+0.58 | Ø 21.40-0.52 | 2.50±0.10 | 2.90+0.20 | 3,70 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z16 | 090680 | Ø 16.40+0.58 | Ø 24.60-0.52 | 2.50±0.10 | 3.10+0.20 | 5,10 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
Stainless steel A4 / 1.4401
| SK-Z | Article No. | DI | DA | S1 | H | Weight/1.000 St. | Pcs. per unit | 3D Download | Request |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SK-Z6 | 096630 | Ø 6.10+0.48 | Ø 9.90-0.36 | 1.40±0.10 | 1.60+0.20 | 0,50 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z8 | 096640 | Ø 8.20+0.58 | Ø 12.70-0.36 | 1.40±0.10 | 1.70+0.20 | 0,90 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z10 | 096650 | Ø 10.20.0.58 | Ø 16.10-0.36 | 1.60±0.10 | 2.00+0.20 | 1,50 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z12 | 096660 | Ø 12.40+0.58 | Ø 18.30-0.52 | 1.80±0.10 | 2.40+0.20 | 2,00 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z14 | 096670 | Ø 14.40+0.58 | Ø 21.40-0.52 | 2.50±0.10 | 2.90+0.20 | 3,70 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| SK-Z16 | 096680 | Ø 16.40+0.58 | Ø 24.60-0.52 | 2.50±0.10 | 3.10+0.20 | 5,10 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
Technical changes reserved
1
Initial material thickness
3D Download
We are happy to provide you with the design files of our discs as STP data. Please enter the information below to download the file.