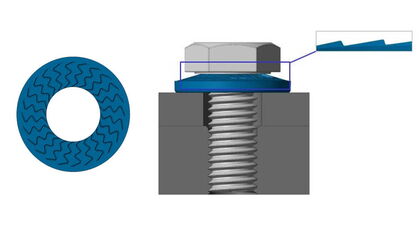
NSK-EElectrical screw connections
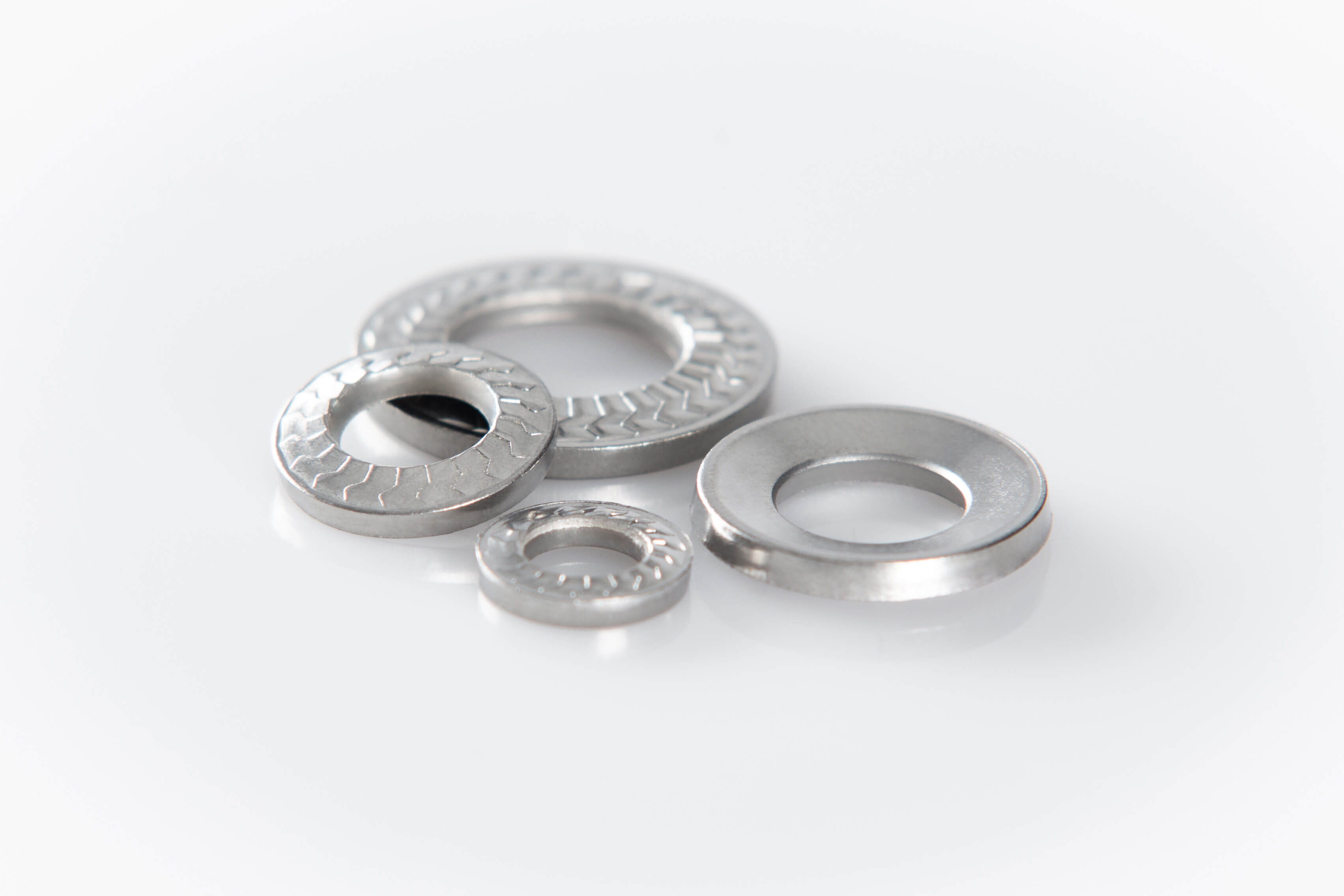

Areas of application
- Electrical contact glands
- Earthing and equipotential bonding applications with conductors (without penetrating insulating layers)
- Fasteners / connections on printed circuit boards
- Fastening solutions with copper, aluminium, stainless steel, plastic materials or coated surfaces and low preload forces
- Circular hole (slotted hole -> NSK-EL)
Special features
- One-piece and easy to install
- Anti-loosening and anti-rotation lock
- Specially adapted to the preload forces of electrical contact screw connections
- Protection of the conductor material and uniform pressure cone
- Complies with the current state of the art, incl. the standard requirements DIN 25201-3, DIN 43673, DIN 46206, DIN EN 50343, DIN EN 60204-1, DIN EN 61439-1, (NEW) DIN EN 17976 (NEW) ...
- Recommended by Deutsche Bahn
Comparison of possible solutions for electrical contact glands
| Spring/profile Locking edge ring1 Spring washer2 with washer |
Wedge disc pairs (flat design) |
Wedge disc pairs (conical design) |
Clamping disc (DIN6796) |
NSK-E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Damage to the mating layer / conductor materials |
|
|
|
|
|
| Uniform contact pressure |
|
|
|
|
|
| Defined / reproducible contact pressure (coefficient of friction) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Compensation of slackening effects3 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Compensation of loosening effects4 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Installation effort and risk |
|
|
|
|
|
| One-piece threadlocking solution5 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Acquisition costs compared to washer DIN 1256 |
|
|
|
|
|
Technical information
| Spring steel C60 EN 1.1211 |
Stainless steel A41 EN 1.4401 |
Other materials EN 1.4547, EN 2.4819, EN 2.4668 (on request) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness / Strength | ≥ 430 HV10 | ≥ 595 N/mm2 | depending on material |
| Coating | Zn/Ni | - | - |
| Corrosion protection | 168h white rust, 720h red rust acc. to DIN EN ISO 9227 NSS | PREN 27 | depending on material |
| Temperature range | -40°C to 150°C | -40°C to 150°C | depending on material |
| Screw quality | max. 8.8 | up to and including A4-80 |
depending on material |
| Dimension range | M3 - M16 | M3 - M16 | as required |
Applications
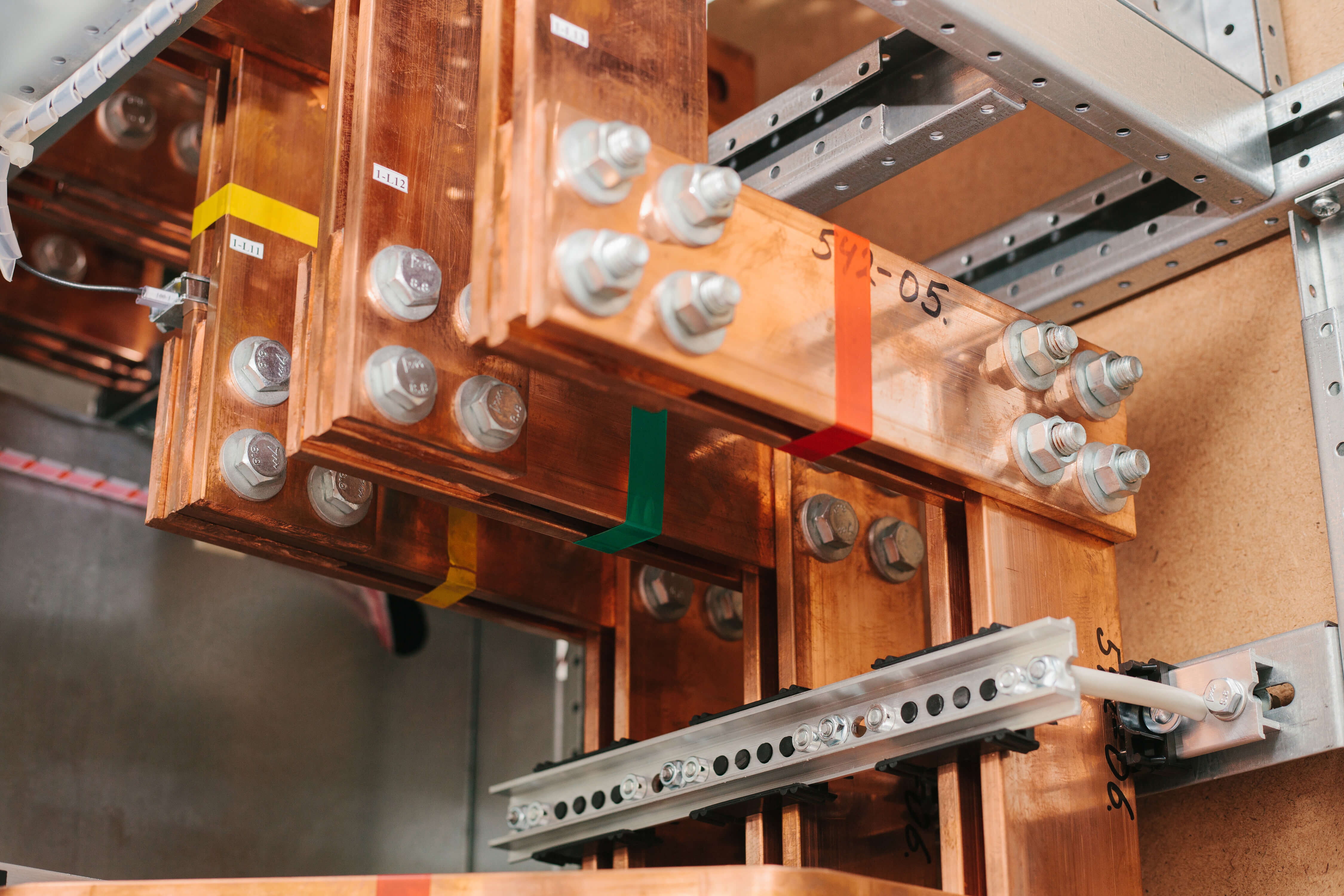



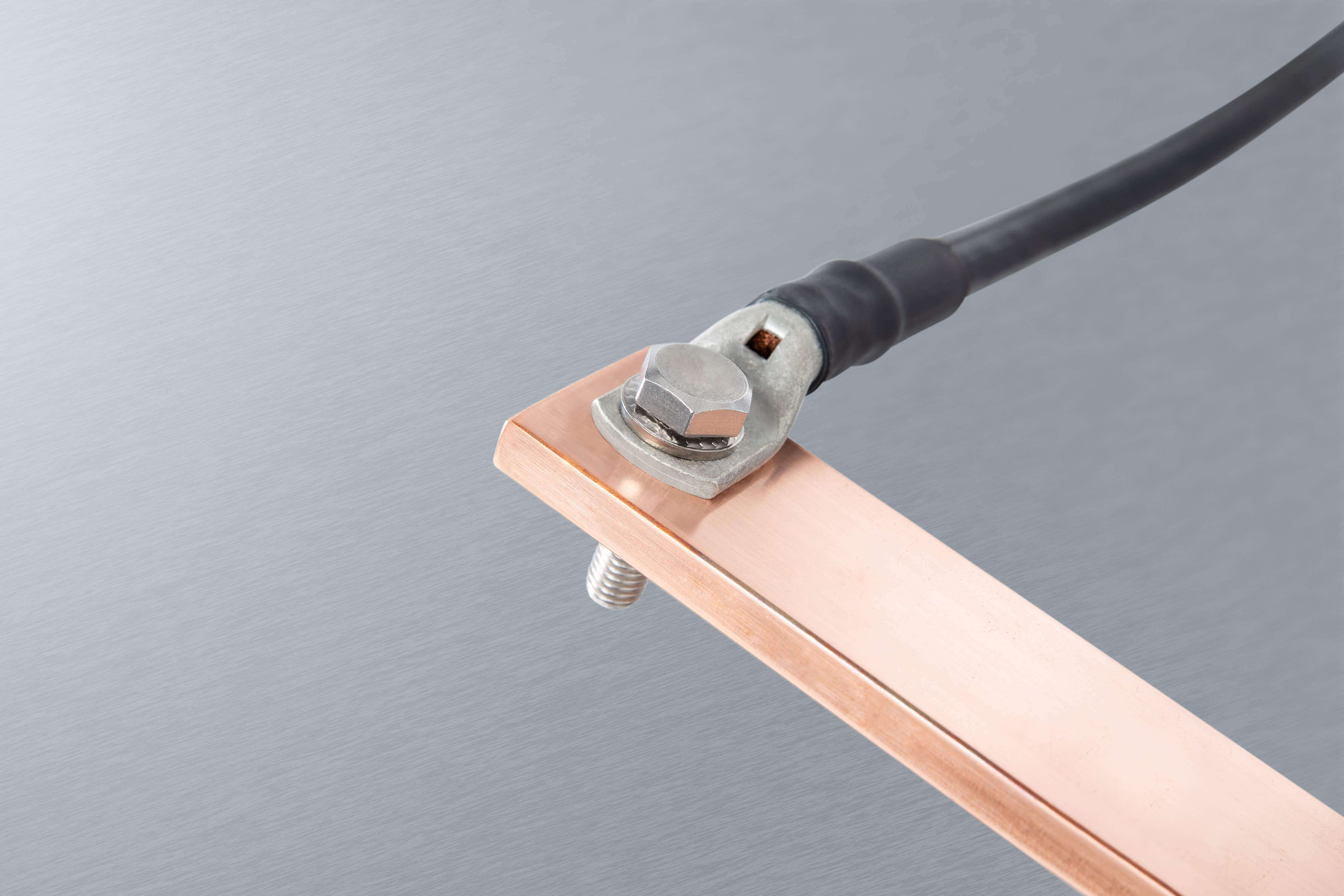
How do electrical contact fittings work?
Current flow
The current flows via the contact surfaces of the conductor materials, not via the screw connection. The screw connection ensures the lowest possible contact resistance with the contact pressure.
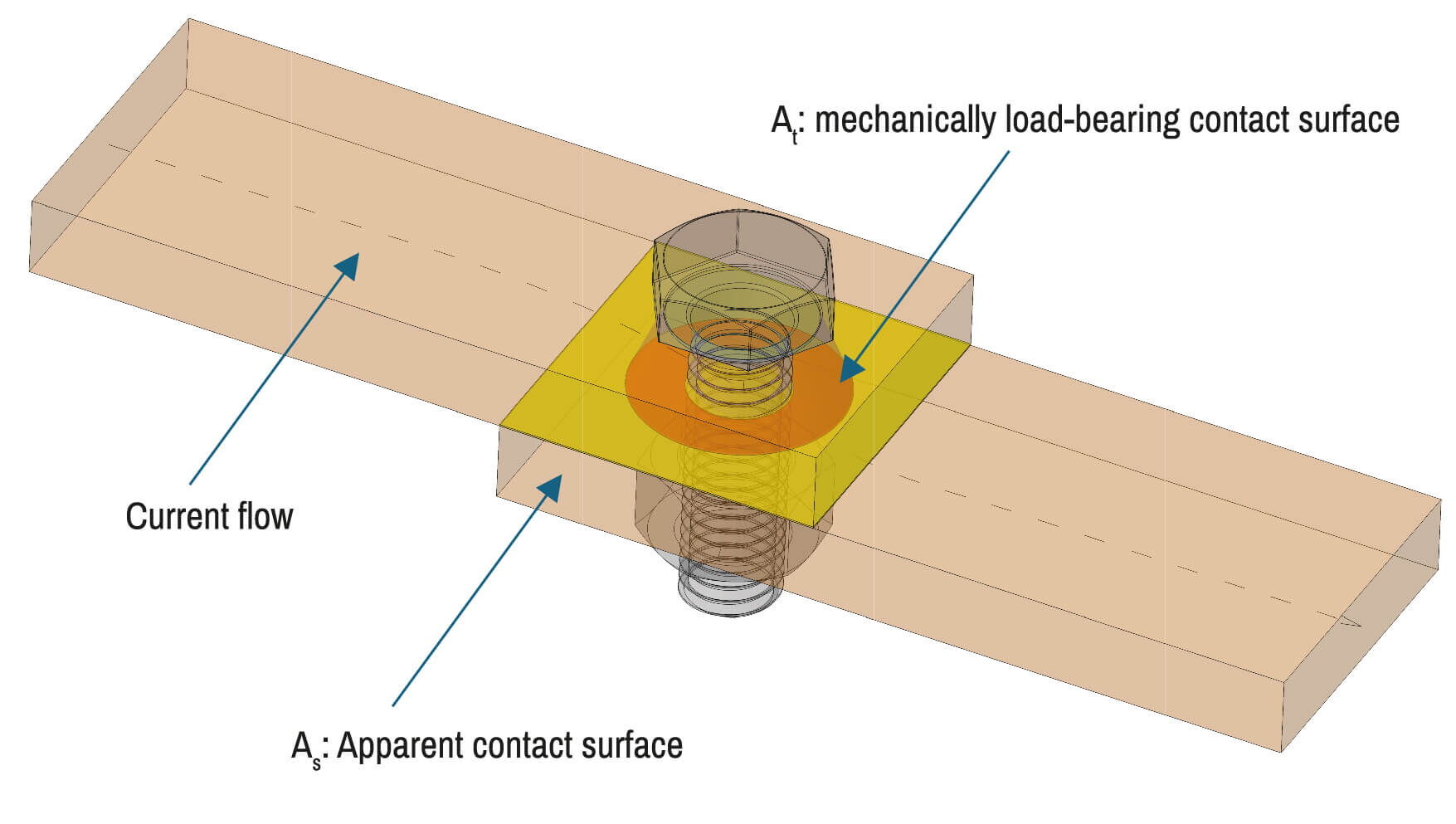
Contact surfaces
The contact resistance of the connection depends on the contact pressure over the entire surface. A low contact resistance / good current flow only exists at the surface areas with high, uniform contact pressure.
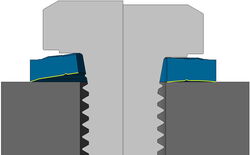
Deformation cone of a centre-braced through-bolt connection (schematic)
What are the special challenges of electrical contact fittings?
- Reduced tightening torques / preload forces
- Due to the lower limit yield stress of the conductor material, only lower preload forces are possible
- Connection-side force reduction of the soft conductor materials
- Stronger setting behaviour of soft conductor materials and coatings
- Long-term behaviour of the material
- Plasticisation and relaxation
- Creep phenomena
- Electrochemical corrosion
- Functional and ambient conditions
- Natural frequencies of the conductors
- Transfer of the vibrations of the overall systems to electrical conductors
- Thermally induced relative movements transverse to the screw axis
- Due to the high expansion coefficients of the conductor materials
- Applies in particular to conductor rails connected at an angle to each other
In the case of electrical contact screw connections, there is a collective of causes that can lead to loosening and unscrewing effects or decreasing contact pressure and heating/short-circuiting.
Why do screw connections come loose?
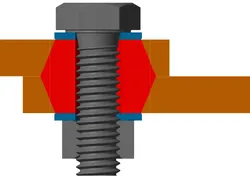
How does an NSK-E work?
Force-locking effect with curved geometry matched to the preload force depending on the strength class
- Increases the flexibility of a bolted joint
- Prevents slackening effects and supports the locking effect against selfacting loosening
Form locking effect due to the interlocking under the screw head or on the nut
- Supports the locking effect against selfacting loosening
Protection of the counter layer
(conductor material (CU/AL), GRP, etc.)
Contact marking NSK-E
(conductor material (CU/AL), GRP, etc.)
Usual contact markings
(conductor material (CU/AL), GRP, etc.)
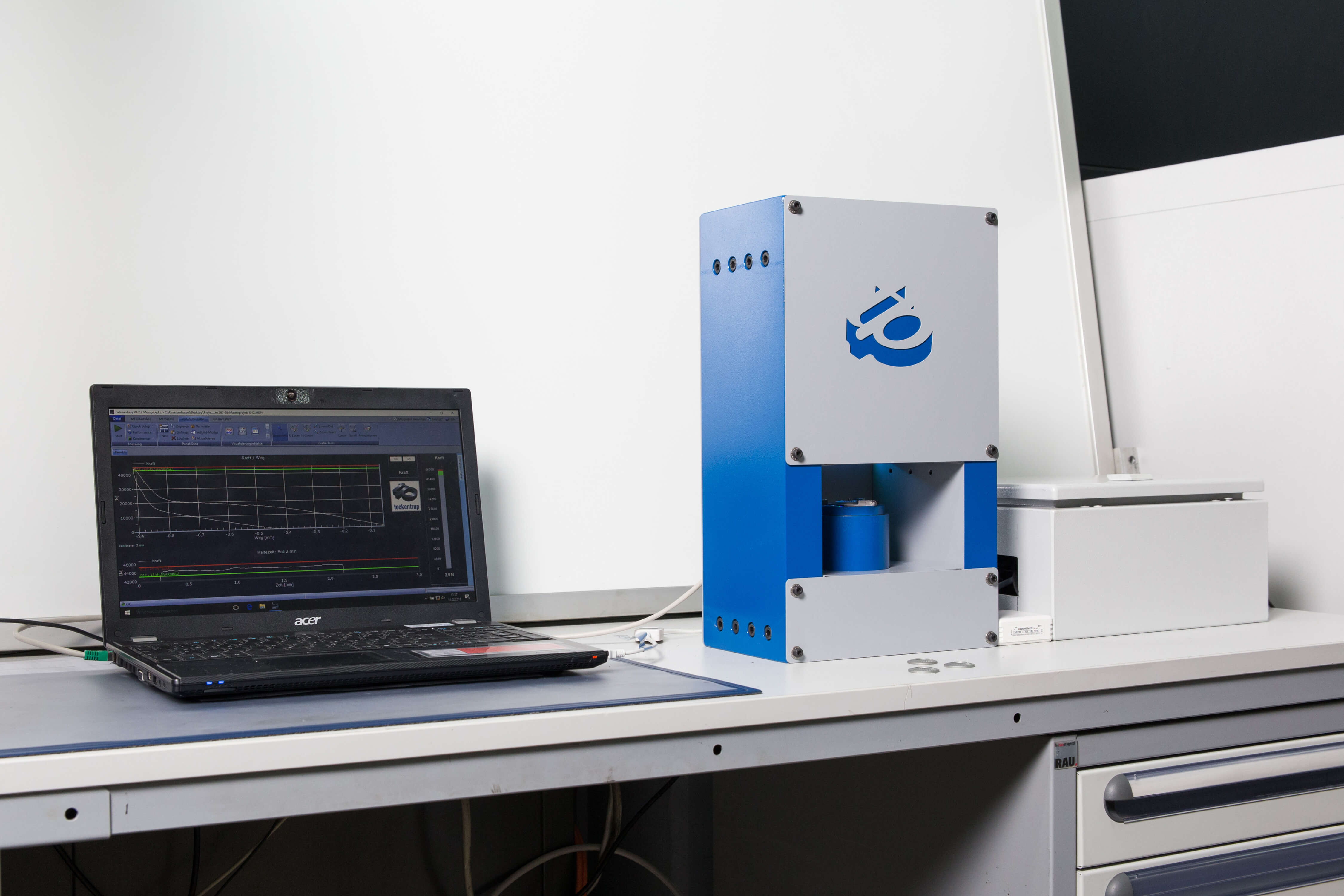
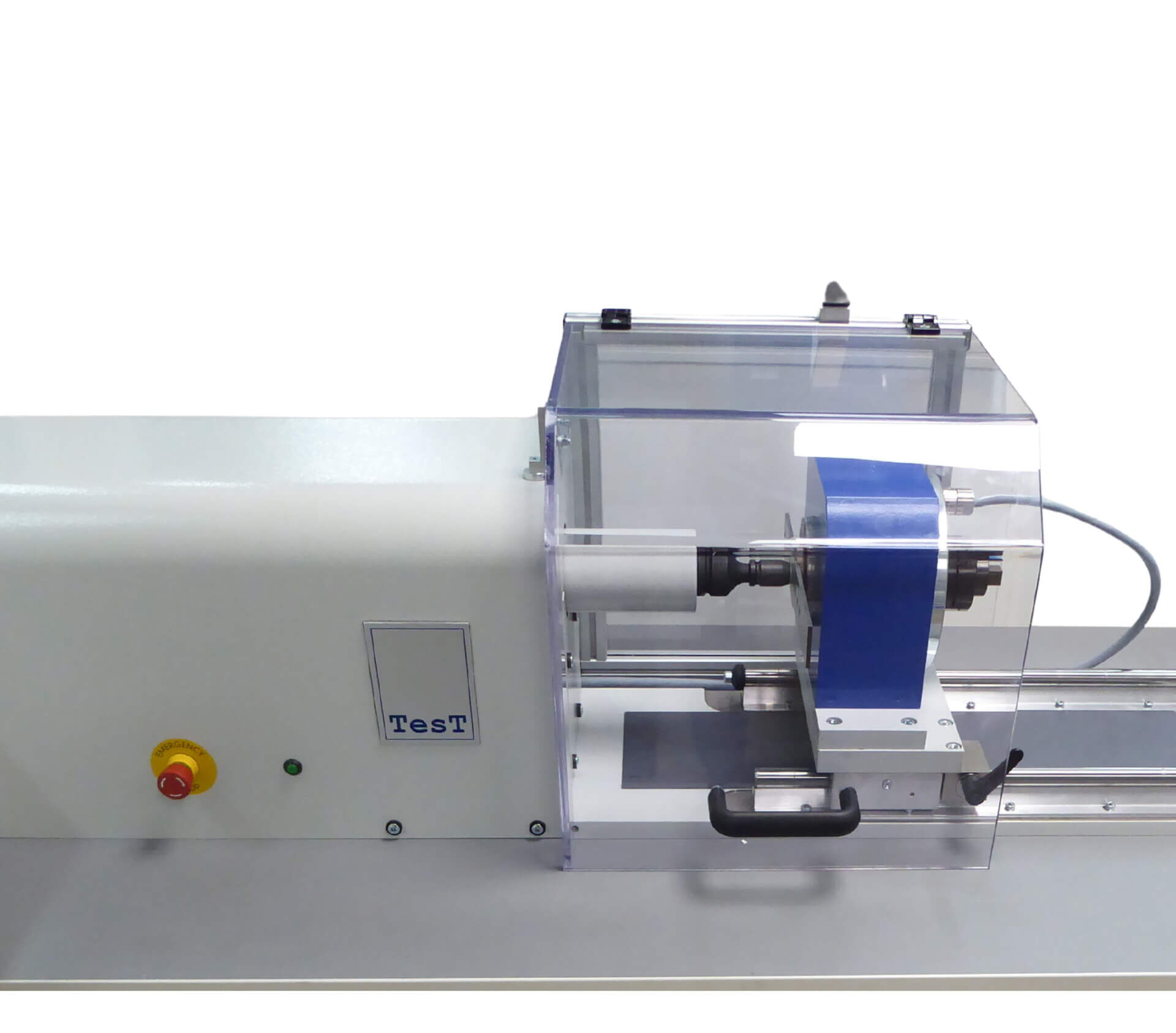
How are NSK-E tested?
Minimum residual spring force test according to DIN 267-26
Force measurement, if the screw connection is relieved by 20μm (Technical specifications for conical spring steel washers for bolted joints)
Friction coefficients are determined in accordance with DIN 16047
The decisive factors for a constant and defined coefficient of friction with low tolerance are:
a.) the form of the connecting element
b.) the surface coating of the connecting element
Vibration test according to DIN 65151 & DIN 25201-4 Annex B.
Application-orientated testing based on the requirements of DIN 25201-3 with samples made of copper material at reduced preload forces.
Uniform pressure cone
The low boundary yield stress of the conductor materials requires a high, uniform contact pressure between the surfaces. Due to the specific shape and design, the washer has:
- a flat form after the tighten process and
- a contact surface with two contact-circuits after the embedding and creeping processes
Spring steel galvanised
| NSK-E | Article No. | DI | DA | S1 | H | Weight/1.000 pcs. | Pcs. per unit | 3D Download | Request |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSK-E3 | 070905 | Ø 3.10+0.35 | Ø 7.10-0.30 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.10+0.20 | 0,25 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E4 | 070910 | Ø 4.10+0.48 | Ø 9.10-0.40 | 1.20±0.05 | 1.30+0.20 | 0,49 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E5 | 070920 | Ø 5.10+0.48 | Ø 10.40-0.52 | 1.20±0.05 | 1.40+0.20 | 0,50 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E6 | 070930 | Ø 6.10+0.48 | Ø 12.10-0.52 | 1.50±0.05 | 1.70+0.20 | 0,90 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E8 | 070940 | Ø 8.20+0.58 | Ø 16.10-0.52 | 1.70±0.05 | 2.00+0.30 | 1,65 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E10 | 070950 | Ø 10.20+0.58 | Ø 20.10-0.52 | 1.80±0.10 | 2.30+0.35 | 2,88 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E12 | 070960 | Ø 12.30+0.58 | Ø 24.10-0.52 | 2.00±0.10 | 2.50+0.35 | 4,80 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E16 | 070980 | Ø 16.30+0.58 | Ø 30.10-0.52 | 2.20±0.10 | 2.80+0.35 | 7,87 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
Stainless steel A4 / 1.4401
| NSK-E | Article No. | DI | DA | S1 | H | Weight/1.000 pcs. | Pcs. per unit | 3D Download | Anfrage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSK-E3 | 076905 | Ø 3.10+0.35 | Ø 7.30-0.40 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.10+0.20 | 0,22 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E4 | 076910 | Ø 4.10+0.48 | Ø 9.40-0.40 | 1.20±0.05 | 1.30+0.20 | 0,43 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E5 | 076920 | Ø 5.10+0.48 | Ø 10.40-0.52 | 1.20±0.05 | 1.30+0.20 | 0,48 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E6 | 076930 | Ø 6.10+0.48 | Ø 12.10-0.52 | 2,10±0.10 | 2.20+0.30 | 1,25 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E8 | 076940 | Ø 8.20+0.58 | Ø 16.10-0.52 | 2.20±0.10 | 2.50+0.30 | 2,27 kg | 1.000 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E10 | 076950 | Ø 10.20+0.58 | Ø 20.10-0.52 | 2.30±0.10 | 2.90+0.35 | 3,85 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E12 | 076960 | Ø 12.20+0.58 | Ø 24.10-0.52 | 2.70±0.10 | 3.10+0.35 | 6,46 kg | 500 | Download | Add to request list |
| NSK-E16 | 076980 | Ø 16.30+0.58 | Ø 30.10-0.52 | 2.90±0.10 | 3.60+0.35 | 10,73 kg | 250 | Download | Add to request list |
3D Download
We are happy to provide you with the design files of our discs as STP data. Please enter the information below to download the file.